Not to be confused with Golden Crescent.
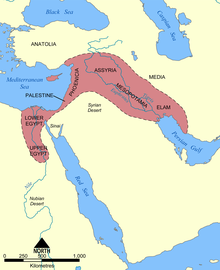
The Fertile Crescent (also known as the Cradle of Civilization) is a crescent-shaped region containing the comparatively moist and fertile land of otherwise arid and semi-arid Western Asia, the Nile Valley and Nile Delta. Having originated in the study of ancient history, the concept soon developed and today retains meanings in international geopolitics and diplomatic relations.
In current usage, all definitions of the Fertile Crescent include Mesopotamia, the land in and around the Tigrisand Euphrates rivers; and the Levant, the eastern coast of the Mediterranean sea. The modern-day countries with significant territory within the Fertile Crescent are Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, Jordan, Israel, Palestine, Egypt, beside the southeastern fringe of Turkeyand the western fringes of Iran.[1][2]
The region is often called the cradle of civilization, as it saw the development of some of the earliest human civilizations, which flourished thanks to the water supplies and agricultural resources available in the Fertile Crescent. Technological advances made in the region include the development of writing, glass, the wheel and the use of irrigation.
Terminology
The term "Fertile Crescent" was popularized by University of Chicago archaeologist James Henry Breasted, beginning with his high school textbooks Outlines of European History in 1914 and Ancient Times, A History of the Early World in 1916.[3] Breasted's 1916 textbook description of the Fertile Crescent:[3]
In current usage, the Fertile Crescent includes Iraq, Kuwait, and surrounding portions of Iranand Turkey, as well as and the rest of the Levantine coast of the Mediterranean Sea, Syria, Jordan, Israel and Lebanon. Water sources include the Jordan River. The inner boundary is delimited by the dry climate of the Syrian Desert to the south. Around the outer boundary are the arid and semi-arid lands of the Caucasus to the North, the Anatolian highlands to the west, and the Sahara Desert to the west.
Languages
Linguistically, the Fertile Crescent was a region of great diversity. Historically, Semitic languages generally prevailed in the lowlands, whilst in the mountainous areas to the east and north a number of generally unrelated languages were found including Elamite, Kassite, and Hurro-Urartian. The precise affiliation of these, and their date of arrival, remain topics of scholarly discussion. However, given lack of textual evidence for the earliest era of prehistory, this debate is unlikely to be resolved in the near future.
The evidence which does exist suggests that already by the third millennium BC, and into the second, several language groups existed. These included:[4][5]
- Sumerian – a non-Semitic language which displays a Sprachbund-type relationship with neighbouring Akkadian
- Semitic languages – Akkadian, Amorite, Aramaic, Ugaritic, Canaanite.
- Hurro-Urartian languages – a small family. (The otherwise isolated Kassite language may be related.)
- Hattic – a language isolate, spoken originally in central Anatolia.
- Indo-European languages – generally believed to be later intrusive languages, such as Hittite and the Indo-Aryan material attested in the Mittani civilization.
(Links of Hurro-Urartian and Hattic with indigenous languages of the Caucasus have frequently been suggested, but are not generally accepted.)
Geography
As crucial as rivers and marshlands were to the rise of civilization in the Fertile Crescent, they were not the only factor in the area's precocity. The area is important as the "bridge" between Africa and Eurasia. This "bridging role" has allowed the Fertile Crescent to retain a greater amount of biodiversity than either Europe or North Africa, where climate changesduring the Ice Age led to repeated extinction events when ecosystems became squeezed against the waters of the Mediterranean Sea. Coupled with the Saharan pump theory, this Middle Eastern land-bridge is of extreme importance to the modern distribution of Old Worldflora and fauna, including the spread of humanity.
The area has borne the brunt of the tectonic divergence between the African and Arabian plates and the converging Arabian and Eurasian plates, which has made the region a very diverse zone of high snow-covered mountains.
Climate and bio-diversity
The Fertile Crescent had many diverse climates, and major climatic changes encouraged the evolution of many "r" type annual plants, which produce more edible seeds than "K" type perennial plants. The region's dramatic variety of elevation gave rise to many species of edible plants for early experiments in cultivation. Most importantly, the Fertile Crescent was home to the eight Neolithic founder crops important in early agriculture (i.e. wild progenitors to emmer wheat, einkorn, barley, flax, chick pea, pea, lentil, bitter vetch), and four of the five most important species of domesticated animals—cows, goats, sheep, and pigs—and the fifth species, the horse, lived nearby.[6]
History
The Fertile Crescent has an impressive record of past human activity. As well as possessing many sites with the skeletal and cultural remains of both pre-modern and early modern humans (e.g. at Kebara Cave in Israel), later Pleistocene hunter-gatherers and Epipalaeolithic semi-sedentary hunter-gatherers (the Natufians), this area is most famous for its sites related to the origins of agriculture. The western zone around the Jordan and upper Euphrates rivers gave rise to the first known Neolithic farming settlements (referred to as Pre-Pottery Neolithic A (PPNA)), which date to around 9,000 BC (and includes sites such as Jericho).
This region, alongside Mesopotamia (which lies to the east of the Fertile Crescent, between the rivers Tigris and Euphrates), also saw the emergence of early complex societies during the succeeding Bronze Age. There is also early evidence from the region for writing and the formation of hierarchical statelevel societies. This has earned the region the nickname "The Cradle of Civilization."
Both the Tigris and Euphrates start in the Taurus Mountains of what is today Turkey. Farmers in southern Mesopotamia had to protect their fields from flooding each year, except northern Mesopotamia which had just enough rain to make some farming possible. To protect against flooding, they made levees.[7]
Since the Bronze Age, the region's natural fertility has been greatly extended by irrigationworks, upon which much of its agricultural production continues to depend. The last two millennia have seen repeated cycles of decline and recovery as past works have fallen into disrepair through the replacement of states, to be replaced under their successors. Another ongoing problem has been salination — gradual concentration of salt and other minerals in soils with a long history of irrigation.
Early domestications
Cereals were already grown in Syria as long as 9,000 years ago.
Prehistoric seedless figs were discovered in the Jordan Valley, suggesting that fig trees were being planted some 11,300 years ago.[8]
Notes and References
- ^ Haviland, William A., et. al (2013). The Essence of Anthropology (3rd ed.). Belmont, California: Wadsworth. p. 104. ISBN 1111833443.
- ^ Ancient Mesopotamia/India. Culver City, California: Social Studies School Service. 2004. p. 4. ISBN 1560041668.
- ^ a b Abt, Jeffrey (2011). American Egyptologist: the life of James Henry Breasted and the creation of his Oriental Institute. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. pp. 193–194, 436. ISBN 978-0-226-0011-04.
Goodspeed, George Stephen (1904). A History of the ancient world: for high schools and academies. New York: Charles Scribner's Sons. pp. 5–6.
Breasted, James Henry (1914). "Earliest man, the Orient, Greece, and Rome". In Robinson, James Harvey; Breasted, James Henry; Beard, Charles A. Outlines of European history, Vol. 1 (PDF). Boston: Ginn. pp. 56–57. "The Ancient Orient" map is inserted between pages 56 and 57.
Breasted, James Henry (1916). Ancient times, a history of the early world: an introduction to the study of ancient history and the career of early man (PDF). Boston: Ginn. pp. 100–101."The Ancient Oriental World" map is inserted between pages 100 and 101.
Clay, Albert T. (1924). "The so-called Fertile Crescent and desert bay". Journal of the American Oriental Society 44: 186–201. doi:10.2307/593554. JSTOR 593554.
Kuklick, Bruce (1996). "Essay on methods and sources". Puritans in Babylon: the ancient Near East and American intellectual life, 1880–1930. Princeton: Princeton University Press. p. 241. ISBN 978-0-691-02582-7.Textbooks...The true texts brought all of these strands together, the most important being James Henry Breasted, Ancient Times: A History of the Early World (Boston, 1916), but a predecessor, George Stephen Goodspeed, A History of the Ancient World (New York, 1904), is outstanding. Goodspeed, who taught at Chicago with Breasted, antedated him in the conception of a 'crescent' of civilization.
- ^ Oxford Handbook of Ancient Anatolia. Ed. Steadman & McMahon. 2011. Pg 233, 522, 556.
- ^ A Companion to the Archaeology of the Ancient Near East. Ed: T Potts, 2012. Pg 28, 570, 584.
- ^ Diamond, Jared. (March 1997). Guns, Germs, and Steel: The Fates of Human Societies. W.W. Norton & Company. ISBN 0-393-03891-2.
- ^ Beck, Roger B.; Black, Linda; Krieger, Larry S.; Naylor, Phillip C.; Shabaka, Dahia Ibo (1999). World History: Patterns of Interaction. Evanston, IL: McDougal Littell. ISBN 0-395-87274-X.
- ^ Genographic Project / The Development of Agriculture nationalgeographic.com
Bibliography
See also
External Links
- Ancient Fertile Crescent Almost Gone, Satellite Images Show – from National Geographic News, May 18, 2001.
Wikipedia





No comments:
Post a Comment