Published Date
Author


References
Sylvain Jeandroz, Agrosup Dijon, France
http://journal.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fpls.2016.00898/full
Author
- 1Institute of Plant Nutritional Physiology and Molecular Biology, College of Resources and Environment, Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, Fuzhou, China
- 2Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Soil Environmental Health and Regulation, College of Resources and Environment, Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, Fuzhou, China
- 3Institute of Materia Medica, Fujian Academy of Medical Sciences, Fuzhou, China
- 4Pomological Institute, Fujian Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Fuzhou, China
- 5The Higher Educational Key Laboratory of Fujian Province for Soil Ecosystem Health and Regulation, Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, Fuzhou, China
Boron (B) toxicity is observed in some citrus orchards in China. However, limited data are available on the molecular mechanisms of citrus B-toxicity and B-tolerance. Using cDNA-AFLP, we identified 20 up- and 52 down-regulated genes, and 44 up- and 66 down-regulated genes from excess B-treated Citrus sinensis and Citrus grandis roots, respectively, thereby demonstrating that gene expression profiles were more affected in the latter. In addition, phosphorus and total soluble protein concentrations were lowered only in excess B-treated C. grandis roots. Apparently, C. sinensis had higher B-tolerance than C. grandis. Our results suggested that the following several aspects were responsible for the difference in the B-tolerance between the two citrus species including: (a) B-excess induced Root Hair Defective 3 expression in C. sinensis roots, and repressed villin4 expression in C. grandis roots; accordingly, root growth was less inhibited by B-excess in the former; (b) antioxidant systems were impaired in excess B-treated C. grandis roots, hence accelerating root senescence; (c) genes related to Ca2+ signals were inhibited (induced) by B-excess in C. grandis (C. sinensis) roots. B-excess-responsive genes related to energy (i.e., alternative oxidase and cytochrome P450), lipid (i.e., Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase 9 and citrus dioxygenase), and nucleic acid (i.e., HDA19, histone 4, and ribonucleotide reductase RNR1 like protein) metabolisms also possibly accounted for the difference in the B-tolerance between the two citrus species. These data increased our understanding of the mechanisms on citrus B-toxicity and B-tolerance at transcriptional level.
Introduction
Boron (B), an essential element for normal growth and development of higher plants, is taken up by roots in the form of boric acid from soil solution. Despite this, B is toxic to higher plants when present in excess (Nable et al., 1997; Chen et al., 2012; Sang et al., 2015). Although B-toxicity is less common than B-deficiency, it is still a serious problem in many agricultural regions across the world. However, the molecular mechanisms on B-toxicity and B-tolerance in higher plants are not fully understood.
In higher plants, B-excess cause impairments of cellular functions and physiological and biochemical processes, such as plant growth (Ayvaz et al., 2012; Guo et al., 2014), hormone balance (Ayvaz et al., 2012, 2015), uptake and use efficiency of other mineral elements (Papadakis et al., 2003; Aquea et al., 2012), leaf photosynthetic electron transport chain (Han et al., 2009), photosynthetic rate (Han et al., 2009; Sheng et al., 2010; Chen et al., 2012; Guo et al., 2014), photosynthetic enzyme activities (Han et al., 2009), reactive oxygen metabolism (Keles et al., 2004; Cervilla et al., 2007; Han et al., 2009), chlorophyll (Chl) and carotenoid (Car) levels (Han et al., 2009; Ayvaz et al., 2012), cell wall biosynthesis (Huang et al., 2016); carbohydrate (Keles et al., 2004; Papadakis et al., 2004a,b; Han et al., 2009), energy (Reid et al., 2004; Guo et al., 2014), nucleic acid (Wang et al., 1995), and nitrogen (N; Cervilla et al., 2009; Chen et al., 2014) metabolisms, and leaf and root structure (Papadakis et al., 2004a,b; Chen et al., 2012; Huang et al., 2014; Mesquita et al., 2016).
Transcriptomic analysis not only offers us the chance to elucidate the molecular mechanisms on plant B-toxicity and B-tolerance but also is very useful for us to obtain B-excess-responsive genes possibly responsible for B-tolerance. There are several studies investigating B-excess-induced alterations of gene profiles in higher plants. Using microarray, Kasajima and Fujiwara (2007) isolated many high-B-induced genes from Arabidopsis thaliana roots and rosette leaves; nine of which were validated in an independent experiment. Using suppression subtractive hybridization (SSH), Hassan et al. (2010) found 111 up-regulated clones showing similar to known proteins from high-B-treated roots of the B-tolerant barely bulk, thereby suggesting that both polyamines and ascorbate–glutathione pathway played a role in the B-tolerance of barely. Padmanabhan et al. (2012) used SSH to isolate 219 and 113 unique B-excess-responsive non-redundant expressed sequence tags (ESTs) from extremely B-tolerant Puccinellia distans and moderately B-tolerant Gypsophila arrostil plants, respectively. In addition to restricting B accumulation in plant tissues via enhancing the expression of efflux transporters similar to barely Bot1, genes related to stress/defense, protein synthesis, cellular organization, and signal transduction had a positive role in the B-tolerance of P. distans. Aquea et al. (2012) obtained 240 up-regulated genes, which mainly function in ABA signaling, ABA response, or cell wall modifications, and 211 down-regulated genes, which are mainly related to glucosinolate biosynthesis, water, or nutrient transport, suggesting that B-toxicity-induced water stress was responsible for root growth inhibition under B-stress. Recently, Tombuloglu et al. (2015) used high-throughput RNA-Seq to examine B-toxicity-induced alterations of gene profiles in barely and observed a total of 14,385 and 11,472 differentially expressed transcripts from high-B-treated roots and leaves, respectively, and concluded that genes involved in cell wall and cytoskeleton, plasma membrane, stress response, and signal transduction played key roles in the B-tolerance of barely. Although the transcriptional responses of herbaceous plants to B-toxicity have been investigated in some details, such data are very limited in woody plants.
In China, B-excess is observed in some citrus orchards. Li et al. (2015) measured the water-soluble B content of 319 soil samples and the B concentration of 319 leaf samples from 319 pummelo (Citrus grandis) orchards located in Pinghe, Zhangzhou, China. Up to 22.9 and 74.8% of orchards were excess in soil water-soluble B and leaf B, respectively. Therefore, it is very important to understand the molecular mechanisms on B-toxicity and B-tolerance of citrus. cDNA-amplified fragment length polymorphism (cDNA-AFLP), which does not need prior sequence information for the amplification, is a highly sensitive and reproducible approach for detecting polymorphisms in DNA. Therefore, cDNA-AFLP has been widely used for the identification of various stress-regulated genes and for the isolation of novel genes (Ditt et al., 2001; Fusco et al., 2005; Craciun et al., 2006; Paun and Schönswetter, 2012; Zhou et al., 2013; Vantini et al., 2015). Previously, we used cDNA-AFLP to assay long-term B-excess-responsive genes in B-tolerant Citrus sinensis and B-intolerant C. grandis leaves and obtained 132 and 68 differentially expressed genes from B-toxic C. grandis and C. sinensis leaves, respectively. Subsequent analysis suggested that the higher mRNA levels of genes involved in photosynthesis in B-toxic C. sinensis leaves were responsible for the higher CO2 assimilation, thus contributing to the B-tolerance of C. sinensis. Some genes related to stress responses also played a role in the B-tolerance of C. sinensis (Guo et al., 2014). In this study, we further examined long-term B-excess-induced alterations of gene profiles revealed by cDNA-AFLP in B-tolerant C. sinensis and B-intolerant C. grandis roots (Guo et al., 2014; Huang et al., 2014; Sang et al., 2015). The objectives were (a) to determine the differences in B-excess-responsive genes between roots and leaves; (b) to explore the mechanisms on B-toxicity and B-tolerance at translational level; and (c) to obtain B-excess-responsive genes possibly contributing to the B-tolerance of C. sinensis.
Materials and Methods
Plant Materials and Experimental Design
Boron-tolerant “Xuegan” (C. sinensis) and B-intolerant “Sour pummel” (C. grandis) seedlings were used in this study. Both seedling culture and B treatments were performed according to Guo et al. (2014). In a word, 13-week-old seedlings grown in 6 L pots containing sand in a greenhouse under natural photoperiod at Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (FAFU), Fuzhou, China (26°5′ N, 119°14′ E), were irrigated every 2 days until dripping with nutrient solution containing 6 mM KNO3, 2 mM NH4H2PO4, 4 mM Ca(NO3)2, 1 mM MgSO4, 10 μM H3BO3, 2 μM ZnSO4, 2 μM MnCl2, 0.5 μM CuSO4, 0.065 μM (NH4)6Mo7O24 20 μM Fe-EDTA, and 10 μM (control) or 400 μM (B-excess) H3BO3 for 15 weeks. Thereafter, about 5-mm long root tips from new white roots were excised and immediately immersed in liquid nitrogen, and then stored at −80°C until being used for the measurements of total soluble proteins and enzyme activities, and cDNA-AFLP and qRT-PCR analysis. The remaining seedlings were used to assay root B and phosphorus (P) concentrations.
Measurements of Root Total Soluble Protein, B, and P Concentrations
Root concentration of total soluble proteins was assayed according to Bradford (1976) after being extracted with 50 mM Na2HPO4–KH2PO4 (pH 7.0) and 5% (w/v) insoluble polyvinylpyrrolidone. There were five replicates per treatments.
For the measurements of root B and P concentrations, fibrous roots were harvested and dried at 70°C. Root B concentration was determined by ICP emission spectrometry after microwave digestion with HNO3 (Wang et al., 2006). Root P concentration was determined according to Ames (1966). There were four replicates per treatments.
RNA Extraction, cDNA Synthesis, and cDNA-AFLP Analysis
Equal amounts of frozen roots from five excess B-treated or control seedlings (one seedling per pot) of C. grandis or C. sinensis were mixed as a biological replicate. There were three biological replicates for each B treatment. Total RNA was extracted from ca. 300 mg of frozen roots using Recalcitrant Plant Total RNA Extraction Kit (Centrifugal column type, Bioteke Corporation, China). cDNA synthesis and cDNA-AFLP analysis were performed according to Guo et al. (2014) and Lu et al. (2015). Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov) were used for the blast analysis of the differentially expressed transcript-derived fragments (TDFs) from excess B-treated C. grandis and C. sinensis roots. TDFs were blasted using BLASTX and BLASTN search engines (http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi), and a TDF was considered to be homologous when it had an E < 0.001 and a similarity ≥50%. Their functional categories were assigned based on the Gene Ontology (http://amigo1.geneontology.org/cgi-bin/amigo/go.cgi) and UniProt (http://www.uniprot.org/) database.
qRT-PCR Analysis
Root total RNA was extracted as described above. qRT-PCR analysis was carried out according to Zhou et al. (2013) and Lu et al. (2015). The sequences of the specific F and R primers designed from the sequences of 15 singleton TDFs using Primer Premier Version 5.0 (PREMIER Biosoft International, CA, USA) were summarized in Table S1. The samples subjected to qRT-PCR were performed in three biological replicates with two technical replicates. Each biological replicate was created by pooling equal roots from five seedlings (one seedling per pot). Citrus actin (GU911361.1) was used as an internal standard for the normalization of gene expression, and roots from control plants were used as a reference sample (set as 1).
Analysis of Root Peroxidase, Catalase, and Lipoxygenase Activities
Peroxidase (POD) and catalase (CAT) were extracted and assayed according to Li et al. (2010). Lipoxygenase (LOX) was assayed by the formation of conjugated dienes from linoleic acid according to Axelrod et al. (1981).
Statistical Analysis
Differences among four treatment combinations were analyzed by two (B levels) × two (species) ANOVA. Means were separated by the Duncan's new multiple range test at P < 0.05. Significant tests for two means (control and B-excess) were carried out by unpaired t-test at P < 0.05 level.
Results
Effects of B-Excess on Root B, P, and Total Soluble Protein Concentrations
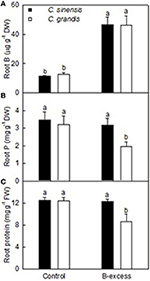
Root B concentration was higher in excess B-treated C. grandis and C. sinensis roots than in controls. Root B level did not differ significantly between the two citrus species at each given B treatment (Figure 1A).
FIGURE 1

Figure 1. Effects of B-excess on root B (A), P (B), and total soluble protein (C) concentrations. Bars represent means ± SD (n = 4). Different letters above the bars indicate a significant difference at P < 0.05.
Root P concentration did not significantly differ among four treatment combinations except for a drop in excess B-treated C. grandis roots (Figure 1B).
Boron excess only lowered total soluble protein concentration in C. grandis roots. Total soluble protein concentration was higher in excess B-treated C. sinensis roots than in excess B-treated C. grandis but was similar between control roots of the two citrus species (Figure 1C).
Root B-Excess-Responsive Genes Revealed by cDNA-AFLP
A total of 256 selective primer combinations were employed to isolate B-excess-responsive genes from B-tolerant C. sinensis and B-intolerant C. grandis roots. A representative silver-stained cDNA-AFLP gel displaying the differentially expressed TDFs in excess B-treated C. grandis and C. sinensis roots was presented in Figure 2. As shown in Table 1, we obtained 5873 TDFs from control and B-toxic C. sinensis and C. grandis roots, 893 (589) of which were presented only in C. grandis (C. sinensis) roots and 4391 were shared by the both.
FIGURE 2

Figure 2. cDNA-AFLP profiles using one EcoR I selective primer and eight Mes I selective primers. One EcoR I selective primer: EcoR I-AT; Eight Mes I selective primers: Mes I-GA, GA, GG, GC, CA, CT, CG, and CC. 1, Control roots of C. grandis; 2, Excess B-treated roots of C. grandis; 3, Control roots of C. sinensis; 4, Excess B-treated roots of C. sinensis. Arrows indicate differentially expressed TDFs.
TABLE 1

Table 1. List of transcript-derived fragments (TDFs) isolated from control and boron (B)-toxic Citrus grandis and Citrus sinensis roots.
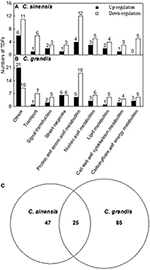
A 1.5-fold cut-off was employed to determine up- and down-regulated TDFs, in addition to a P-value of < 0.05. According to the two criteria, we identified 294 B-excess-responsive TDFs from C. grandis and C. sinensis roots. After sequencing all these TDFs, we obtained readable sequences from 241 TDFs, 157 of which shared identity with genes encoding known, putative, uncharacterized, predicted, hypothetical, or unnamed proteins, and 84 showed no significant matches (Table 1). The 157 matched TDFs were related to carbohydrate and energy metabolism, cell wall and cytoskeleton metabolism, lipid metabolism, nucleic acid metabolism, protein and amino acid metabolism, stress response, signal transduction, transport, and others (Table 2 and Figures 3A,B). As shown in Tables 1, 2 and Figure 3C, most of these matched B-excess-responsive TDFs only presented in C. sinensis (47) or C. grandis (85) roots, only 25 TDFs were shared by the both. Obviously, long-term B-excess-induced alterations of gene profiles greatly differed between C. sinensis and C. grandis roots.
TABLE 2

Table 2. Homologies of differentially expressed cDNA-AFLP fragments with known gene sequences in database using BLASTN algorithm along their expression patterns in excess B-treated C. grandis (CG) and Citrus sinensis (CS) roots.
FIGURE 3

Figure 3. Functional classification of differentially expressed TDFs under B-excess in Citrus grandis (A) and Citrus sinensis roots (B) and Venn diagram analysis of differentially expressed TDFs in citrus roots (C). Functional classification was performed based on the information reported for each sequence by The Gene Ontology (http://amigo1.geneontology.org/cgi-bin/amigo/go.cgi) and Uniprot (http://www.uniprot.org/).
qRT-PCR Validation of Root Differentially Expressed TDFs Revealed by cDNA-AFLP
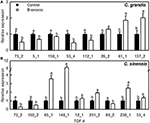
As shown in Figure 4, we selected eight and nine TDFs from C. grandis and C. sinensis roots, respectively, for qRT-PCR analysis in order to examine their expression profiles obtained by cDNA-AFLP. Except for TDFs #137_2 and 53_4 in C. grandis roots, the expression patterns of the other TDFs produced by qRT-PCR agreed with the data obtained by cDNA-AFLP.
FIGURE 4

Figure 4. Relative expression levels of TDFs from Citrus grandis (A) and Citrus sinensis (B) roots. qRT-PCR was run in three biological replicates with two technical replicates. Citrus actin (GU911361.1) was employed as an internal standard, and roots from control plants were used as a reference sample (set as 1). Bars represent means ± SD. Different letters above the bars indicate a significant difference at P < 0.05.
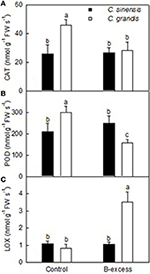
Analysis of Enzymes for Three Differentially Expressed TDFs
We assayed the activities of enzymes for three B-excess-responsive TDFs in C. sinensis and C. grandis roots. The enzyme activities did not match fully with the gene expression levels (Table 2 and Figure 5). The discrepancy between the both means that post-modifications (PTMs) might influence these enzyme abundances and their activities. In addition, all these enzymes are composed of two or more isoenzymes, which might be responsible for the discrepancy between gene expression levels and enzyme activities.
FIGURE 5

Figure 5. Effects of B-excess on root CAT (A), POD (B) and LOX (C) activities. Bars represent means ± SD (n = 4). Different letters above the bars indicate a significant difference at P < 0.05.
Discussion
We isolated more B-excess-responsive TDFs from C. grandis roots than from C. sinensis, demonstrating that B-excess affected gene expression more in B-intolerant C. grandis roots than in B-tolerant C. sinensis roots (Tables 1, 2). This agrees with our data that B-excess only lowered P and total soluble protein concentrations in C. grandis roots (Figures 1B,C) and also agrees with our report that more B-excess-responsive TDFs were obtained from C. grandis leaves than from C. sinensis leaves (Guo et al., 2014). Despite this, great differences existed in B-excess-induced alterations of gene profiles between roots and leaves. For example, most of B-excess-responsive TDFs were identified only from roots or leaves, and only three TDFs with the same genebank ID (i.e., BAD94010.1, NP_564576.1, and XP_003614394.1) were isolated from roots and leaves of C. sinensis and C. grandis. Moreover, the responses of the three TDFs to B-excess differed between leaves and roots (Table 2; Guo et al., 2014).
Effects of B-Excess on Root Carbohydrate and Energy Metabolism
As shown in Table 2, the mRNA levels of three TDFs encoding cytochrome c oxidase subunit Vb (TDF #231_1), NADH dehydrogenase subunit 4 (TDF #101_5), and electron transfer flavoprotein-ubiquinone oxidoreductase (TDF #41_2), the components of the mitochondrial respiratory chain, and of two TDFs encoding pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 α subunit (TDF #98_2) and PK (TDF #53_4) involved in glycolysis were lowered in excess B-treated C. sinensis roots, implying that respiration was impaired in these roots. Similarly, both PK (TDF #53_4) and phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK, TDF #185-1) related to glycolysis were inhibited in excess B-treated C. grandis roots. Interestingly, the expression of alternative oxidase (AOX, a cyanide-insensitive terminal oxidase) gene (TDF #150_1) was also down-regulated in excess B-treated C. grandis roots. Unlike the cytochrome pathway, the AOX pathway, which is cyanide-insensitive and can operate when the cytochrome pathway is restricted, plays a role in inhibiting ROS production in plant mitochondria (Popov et al., 1997; Purvis, 1997; Maxwell et al., 1999; Zidenga et al., 2012). Cytochrome P450s (CytoP450s), a superfamily of monooxygenases, have a key role in (a)biotic stresses. We found that CytoP450 (TDF #137_2) was repressed in excess B-treated C. grandis roots, as obtained on B-toxic Arabidopsis roots (Aquea et al., 2012). Transgenic potato and tobacco plants expressing CytoP450 displayed increased monooxygenase activity and enhanced tolerance to oxidative stress after herbicide treatment (Gorinova et al., 2005). Therefore, B-excess-induced down-regulation of AOX and CytoP450 in C. grandis roots might contribute to the less B-tolerance of C. grandis.
Effects of B-Excess on Root Cell Wall and Cytoskeleton Metabolism
Cell wall and cytoskeleton metabolism were altered in excess B-treated C. sinensis and C. grandis roots, as indicated by B-excess-induced alterations of 10 related genes (i.e., 65_1, 151_2, 37_2, 99_2, 50_1, 26_1, 231_3, 138_1, 249_1, and 253_1; Table 2). Similar results have been obtained on excess B-treated citrus leaves (Guo et al., 2014; Sang et al., 2015). This agrees with the reports that B-toxicity affected citrus root cell walls (Huang et al., 2014) and that B-toxicity disturbed actin filament organization, thus impairing the directional transport of cell wall materials and cell wall construction in Malus domestica pollen tubes (Fang et al., 2016). Root Hair Defective 3 (RHD3), a gene encoding a putative GTP-binding protein, is required for actin organization, cell wall biosynthesis, and normal cell expansion in Arabidopsis roots (Wang et al., 2002; Hu et al., 2003). Overexpression of PeRHD in poplar led to less formation of adventitious roots, better-developed lateral roots, and more and longer root hairs (Xu et al., 2012). B-excess-induced up-regulation of RHD3 in C. sinensis roots might be an adaptive response by maintaining root normal growth and development. By contrast, villin 4 (TDF #50_1), an actin filament bundling protein gene, was down-regulated in excess B-treated C. grandis roots (Table 2). Zhang et al. (2011) demonstrated that Arabidopsis villin 4 was required for normal root hair growth through regulating the organization of actin bundles. The down-regulation of villin 4 implied that B-excess impaired actin organization in C. grandis roots, thus affecting the root growth. The differences in Al-induced alterations of root cell wall and cytoskeleton metabolism between the two citrus species might be responsible for the greater decrease in root dry weight in B-toxic C. grandis seedlings relative to B-toxic C. sinensis ones (Guo et al., 2014).
Effects of B-Excess on Root Lipid Metabolism
We found that all these differentially expressed TDFs (i.e., TDFs #183_2, 249_2, 24_2, 53_3, 129_3, 150_2, 89_2, and 103_6) related to lipid metabolism were inhibited in excess B-treated C. grandis and C. sinensis roots except for three TDFs (i.e., TDFs #44_1, 9_1, and 42_1; Table 2), implying that lipid metabolism pathway in these roots was upset. Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase (GPAT), the first enzyme for the biosynthesis of glycerolipids in all organisms, plays crucial roles in basic cellular metabolism. AtGPAT9 is required for the biosynthesis of membrane lipids and oils. A knockout mutant of AtGPAT9 was homozygous lethal (Shockey et al., 2016). We found that GPAT9 (TDF #183_2) was down-regulated in excess B-treated C. grandis roots (Table 2), suggesting that B-toxicity impaired membrane lipid biosynthesis, thus lowering B-tolerance of C. grandis.
Lipoxygenase (LOX) reactions may initiate the generation of ROS, thus leading to the loss of membranes (Pérez-Gilabert et al., 2001). Inal et al. (2009) found that B-excess increased malondialdehyde (MDA) level and LOX activity, and silicon (Si) enhanced B-tolerance by decreasing B-excess-induced increases in MDA level and LOX activity in barely. B-excess down-regulated (did not significantly affect) LOX expression in C. grandis (C. sinensis) roots (Table 2) but increased (did not significantly affect) LOX activity in C. grandis (C. sinensis) roots (Figure 5C). Therefore, the observed higher LOX activity might lower the B-tolerance of C. grandis.
We found that citrus dioxygenase (TDF #9_1) was up-regulated in excess B-treated C. sinensis roots (Table 2). Alpha-dioxygenase (α-DOX) functions in protecting tissues against oxidative damage and cell death (Tirajoh et al., 2005). Therefore, citrus dioxygenase might be involved in the B-tolerance of C. sinensis.
Effects of B-Excess on Root Nucleic Acid Metabolism
Boron-toxicity affects nucleic acid metabolic process in higher plants (Kasajima and Fujiwara, 2007; Sakamoto et al., 2011; Guo et al., 2014). As expected, three up- (i.e., TDFs #140_2, 129_1 and 148_1) and five down-regulated (i.e., TDFs #82_1, 28_1, 131_4, 60_1 and 246_1) TDFs, and three up- (i.e., TDFs #79_1, 123_2 and 81_3) and six down-regulated (TDFs #246_1, 195_1, 133_4, 134_1, 142_1, and 252_1) TDFs related to nucleic acid metabolism were isolated from excess B-treated C. sinensis and C. grandis roots, respectively (Table 2). Histone deacetylases and histone acetyltransferases, which catalyze histone acetylation and deacetylation, respectively, play a key role in the regulation of gene and genome activity. Arabidopsis histone deacetylase 19 (AtHDA19 or AtHD1) plays a role in plant growth and development. Reduction in AtHDA19 expression by T-DNA insertion or antisense inhibition in Arabidopsis caused various developmental abnormalities such as suppression of apical dominance, early senescence, and flower defects (Tian and Chen, 2001; Tian et al., 2003). Recently, Chen et al. (2015) obtained a total of 86 P-deficiency-responsive genes, which showed lower expression in AtHDA19-RNAi Arabidopsis plants relative to 35S:AtHDA19 lines. Kaya et al. (2009) observed that high-B-treated tomato leaves had lower P concentration, and that supplementary P alleviated high-B-induced decreases in plant growth and fruit yield. B-toxicity decreased P uptake in wheat (Singh et al., 1990). Therefore, excess B-induced up-regulated of HDA19 (TDF #140_2) in C. sinensis roots (Table 2) might be an adaptive response by the maintenances of P homeostasis. This agrees with our report that B-toxicity only reduced P level in C. grandis leaves (Guo et al., 2014) and roots (Figure 1B). Similarly, histone H4 (TDF #129_1) was up-regulated in excess B-treated C. sinensis roots (Table 2), which agrees with the reports that histone H4 was induced in Al-toxic rice roots (Mao et al., 2004) and Al-toxicity increased B level and decreased P level in plant roots, stems, and leaves (Jiang et al., 2009a,b). Histones H2A, H2B, H3, and H4, the core component of nucleosome, play crucial roles in chromosomal stability, gene regulation, and DNA repair and replication (Turner, 2002; Drury et al., 2012; Zhu et al., 2012). Sakamoto et al. (2011) demonstrated that plant condensin II played a crucial role in the tolerance of Arabidopsis to B-toxicity by alleviating DNA damage. Therefore, the up-regulation of histone H4 in excess B-treated C. sinensis roots (Table 2) might contribute to the B-tolerance of C. sinensis by preventing genome from damage resulting from B-excess.
Ribonucleotide reductase (RNR), an enzyme comprising two R1 and two R2, plays a key role in DNA repair and replication (Chabouté et al., 1998; Wang and Liu, 2006). The down of RNR1 like protein (TDF #195_1) in excess B-treated C. grandis roots (Table 2) implied that B-toxicity impaired DNA repair and replication, thus lowering the B-tolerance of C. grandis. Similarly, the expression levels of phosphoribosylaminoimidazole carboxylase/AIR carboxylase (TDF #133_4) involved in nucleotide biosynthesis were down-regulated in excess B-treated C. grandis roots.
Effects of B-Excess on Root Protein and Amino Acid Metabolism
As shown in Table 2, we isolated 10 down-regulated (i.e., TDFs #85_2, 132_3, 73_2, 86_1, 112_1, 27_1, 62_1, 118_5, 41_1, and 24_1) and three up-regulated (i.e., TDFs #42_3, 230_1, and 61_1) TDFs involved in protein degradation, two down-regulated TDFs (i.e., TDFs #253_4 and 184_1,) involved in protein folding and stability, five up-regulated (i.e., TDFs #12_1, 121_2, 9_3, 64_2, and 140_1) and six down-regulated (i.e., TDFs #48_1, 246_5, 153_2, 80_2, 38_1, and 14_2) TDFs involved in protein biosynthesis, and four down-regulated TDFs (i.e., TDFs #229_1, 144_2, 5_1, and 229_2) involved in amino acid metabolism. Obviously, protein and amino acid metabolism was impaired in B-toxic citrus roots.
Effects of B-Excess on Root Stress-Related Gene Expression
Boron-excess causes the accumulation of ROS, thus resulting in oxidative and membrane damage in plant roots and leaves (Cervilla et al., 2007; Pandey and Archana, 2013; Martínez-Cuenca et al., 2015). An antioxidant response has been suggested to abate B-toxic damage in some higher plants (Gunes et al., 2006). Here, we isolated one up-regulated homogentisate phytyltransferase 1 (HPT1; TDF #182_3) from excess B-treated C. grandis and C. sinensis roots (Table 2). HPT catalyzes the committed step in the biosynthesis of tocopherol (vitamin E). Collakova and DellaPenna (2003) showed that transgenic Arabidopsis plants overexpressing HPT1 had an elevated total tocopherol level in seed and leaves. The up-regulation of HPT1 agrees with the increased requirement for the detoxification of ROS in excess B-treated C. grandis and C. sinensis roots. In addition, Obg-like ATPase 1 (YchF1; TDF #64_1), a negative regulator of the antioxidant response (Cheung et al., 2013), was down-regulated in excess B-treated C. grandis roots. However, POD (TDF #99_3) in C. grandis roots and CAT (TDF #231_5) in C. grandis and C. sinensis roots were down-regulated by B-excess. Enzyme activity analysis showed that B-excess lowered CAT and POD activities in C. grandis roots but did not significantly affect their activities in C. sinensis roots (Figures 5A,B). Besides, the expression level of an antioxidant protein gene (Xu and Møller, 2010; Xu et al., 2010), DJ-1 family protein (TDF #30_1) was reduced in excess B-treated C. grandis roots (Table 2). Obviously, excess B-treated C. sinensis roots kept higher antioxidant capacity than excess B-treated C. grandis roots.
Two putative senescence-associated protein genes (i.e., TDFs #131_1 and 17_1) were induced by B-excess in C. grandis roots (Table 2), suggesting that senescence was accelerated in these roots. This agrees with our report that B-excess affected root growth more in C. grandis than in C. sinensis seedlings (Guo et al., 2014). Similarly, autophagic cell death might be accelerated in excess B-treated C. grandis roots, as indicated by the enhanced expression level of WD repeat phosphoinositide-interacting-like protein (WILP; TDF #104_3) in these roots (Table 2). This agrees with our report that B-excess led to cell death in C. grandis roots (Huang et al., 2014).
Effects of B-Excess on Root Signal Transduction
Calcium (Ca) signaling plays vital roles in plant responses to various stresses (Knight, 2000). Ca can alleviate B-toxicity and high-B inhibits Ca uptake in higher plants (Singh et al., 1990; Turan et al., 2009; Siddiqui et al., 2013). Hence, genes related to Ca2+ signal transduction should be altered in excess B-treated citrus roots. As expected, we isolated one up-regulated TDF: ATP/GTP/Ca2+ binding protein [also called as mitochondrial Rho GTPase (MIRO)] from B-toxic C. sinensis roots (Table 2). Jayasekaran et al. (2006) found that the transcript level of MIRO2 was elevated in ABA- and salt-treated Arabidopsis plants, and that the knock-out mutants of MIRO2 were less tolerance to ABA, salt, and osmotic treatments than the wild-type. By contrast, we only isolated three down-regulated TDFs (i.e., TDFs #80_3, 67-2, and 35_2) involved in Ca signals from B-toxic C. grandis roots. Therefore, Ca2+-mediated signal played a role in the tolerance of citrus plants to B-toxicity.
Effects of B-Excess on Transport Processes in Root Cells
As shown in Table 2, the mRNA levels of all the 13 differentially expressed TDFs related to cellular transport were reduced in excess B-treated C. grandis and C. sinensis roots except for one up-regulated H+-ATPase 4 (AHA4, TDF #251_2), indicating that the transport of some substances (i.e., ion and proteins) was altered in these roots. This disagrees with our report that most of the differentially expressed genes involved in cellular transport were up-regulated in excess B-treated C. grandis leaves and three up- and three down-regulated genes were isolated from excess B-treated C. sinensis leaves (Guo et al., 2014).
ABC transporter I family member 20 (ABCI20; TDF #183_2) was down-regulated in excess B-treated C. grandis roots (Table 2). This agrees with our report that ABC1 family protein (AT5g24810) was repressed in high-B-treated C. grandis leaves (Guo et al., 2014). In eukaryotic organisms, ABC transporters have been shown to play a role in the efflux (extracellular or intracellular into the vacuoles) of potentially toxic compounds (i.e., heavy metals, alkaloids, and organic anions; Gaedeke et al., 2001). Transgenic Arabidopsis plants overexpressing AtPDR8 encoding an ABC transporter displayed higher Cd- and Pb-tolerance accompanied by less accumulation of Cd in the shoots or roots. By contrast, mutants were less tolerance to both the metals accompanied by more accumulation of Cd (Kim et al., 2007). Therefore, the down-regulation of ABCI20 and ABC1 family protein in roots and leaves might reduce the efflux of B from the PM, thus increasing free B level and lowering C. grandis B-tolerance. Interestingly, middle leaves from excess B-treated C. grandis seedlings displayed more free B and less bound B than those from C. sinensis, but free B and bound B in excess B-treated roots did not significantly differ between the two citrus species (Huang et al., 2014). Previous studies showed that C. sinensis had defective nodulin-26-like intrinsic protein 2 (NIP2) gene, which is involved in influx of Si, B, and other metalloids (Schnurbusch et al., 2010; Deshmukh et al., 2015). Therefore, NIP2 could be involved in compartmentation of B differently among this species. However, B-excess did not alter NIP2 expression in citrus roots, suggesting that other transporters played a role in citrus compartmentation of B or that NIP2 was regulated at the post-translational level.
Conclusions
We used cDNA-AFLP to investigate comparatively the effects of B-excess on gene profiles in B-tolerant C. sinensis and B-intolerant C. grandis roots, and isolated 20 up- and 52 down-regulated, and 44 up- and 66 down-regulated TDFs from excess B-treated C. sinensis and C. grandis roots, respectively, thereby demonstrating that gene expression was less affected in the former than in the latter. Besides, B-excess only lowered P and total soluble protein concentrations in C. grandis roots. Obviously, C. sinensis seedlings had higher B-tolerance than C. grandis ones. Our results suggested that the following several aspects led to the difference in the B-tolerance between the both, including: (a) AOX and CytoP450 were down-regulated only in excess B-treated C. grandis roots; (b) B-excess up-regulated RHD3 in C. sinensis roots and down-regulated villin4 in C. grandis roots, and accordingly, root dry weight was less reduced by B-excess in the former; (c) antioxidant systems were impaired in excess B-treated C. grandis roots, hence accelerating root senescence; (d) TDFs involved in Ca2+ signals were down-regulated in excess B-treated C. grandis roots and up-regulated in excess B-treated C. sinensis roots. In addition, B-excess-responsive genes related to lipid (i.e., GPAT9 and citrus dioxygenase) and nucleic acid (i.e., histone deacetylase 19, histone 4, and RNR1 like protein) metabolisms also possibly contributed to the difference in the B-tolerance between the both. Our data provided some new clues for our understanding of the molecular mechanisms on citrus B-toxicity and B-tolerance.
Author Contributions
PG carried out most of the experiments and drafted the manuscript. YQ participated in the design of the study. LY participated in the design of the study and coordination. XY participated in the measurement of B and P. JH participated in the statistical analysis. LC designed and directed the study and revised the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
Our work was funded by the earmarked fund for China Agriculture Research System (No. CARS-27).
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: http://journal.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fpls.2016.00898
References
Ames, B. N. (1966). Assay of inorganic phosphate, total phosphate and phosphatase. Meth. Enzymol. 8, 115–118. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(66)08014-5
Chen, M., Mishra, S., Heckathorn, S. A., Frantz, J. M., and Krause, C. (2014). Proteomic analysis of Arabidopsis thaliana leaves in response to acute boron deficiency and toxicity reveals effects on photosynthesis, carbohydrate metabolism, and protein synthesis. J. Plant Physiol. 171, 235–242. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2013.07.008
Craciun, A. R., Courbot, M., Bourgis, F., Salis, P., Saumitou-Laprade, P., and Verbruggen, N. (2006). Comparative cDNA-AFLP analysis of Cd-tolerant and -sensitive genotypes derived from crosses between the Cd hyperaccumulator Arabidopsis halleri and Arabidopsis lyrata ssp. petraea. J. Exp. Bot. 57, 2967–2983. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erl062
Jiang, H. X., Tang, N., Zheng, J. G., and Chen, L. S. (2009b). Antagonistic actions of boron against inhibitory effects of aluminum toxicity on growth, CO2assimilation, ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase, and photosynthetic electron transport probed by the JIP-test, of Citrus grandis seedlings. BMC Plant Biol. 9:102. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-9-102
Li, Q., Chen, L. S., Jiang, H. X., Tang, N., Yang, L. T., Lin, Z. H., et al. (2010). Effects of manganese-excess on CO2 assimilation, ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase, carbohydrates and photosynthetic electron transport of leaves, and antioxidant systems of leaves and roots in Citrus grandis seedlings. BMC Plant Biol. 10:42. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-10-42
Papadakis, I. E., Dimassi, K. N., Bosabalidis, A. M., Therios, I. N., Patakas, A., and Giannakoula, A. (2004a). Effects of B excess on some physiological and anatomical parameters of ‘Navelina’ orange plants grafted on two rootstocks. Environ. Exp. Bot. 51, 247–257. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2003.11.004
Keywords: boron-excess, cDNA-AFLP, Citrus grandis, Citrus sinensis, roots
Citation: Guo P, Qi Y-P, Yang L-T, Ye X, Huang J-H and Chen L-S (2016) Long-Term Boron-Excess-Induced Alterations of Gene Profiles in Roots of Two Citrus Species Differing in Boron-Tolerance Revealed by cDNA-AFLP. Front. Plant Sci. 7:898. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00898
Received: 26 March 2016; Accepted: 07 June 2016;
Published: 24 June 2016.
Published: 24 June 2016.
Edited by:
Jianjun Chen, University of Florida, USA
Reviewed by:
Rupesh Kailasrao Deshmukh, Laval University, CanadaSylvain Jeandroz, Agrosup Dijon, France
Copyright © 2016 Guo, Qi, Yang, Ye, Huang and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Li-Song Chen, lisongchen2002@hotmail.com
For further details log on website :http://journal.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fpls.2016.00898/full
 Peng Guo
Peng Guo Yi-Ping Qi
Yi-Ping Qi Lin-Tong Yang
Lin-Tong Yang Xin Ye
Xin Ye Jing-Hao Huang
Jing-Hao Huang Li-Song Chen
Li-Song Chen




No comments:
Post a Comment